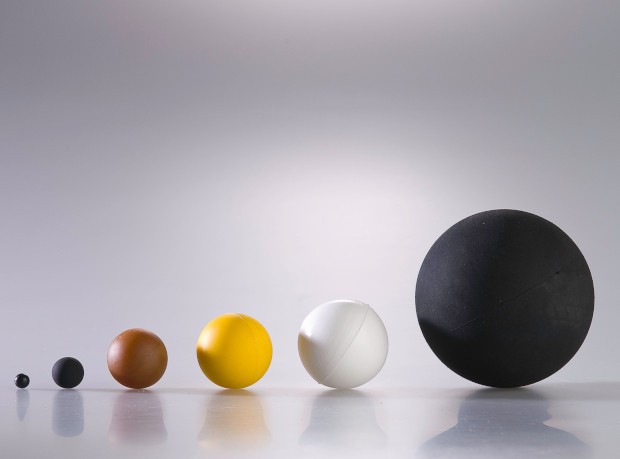
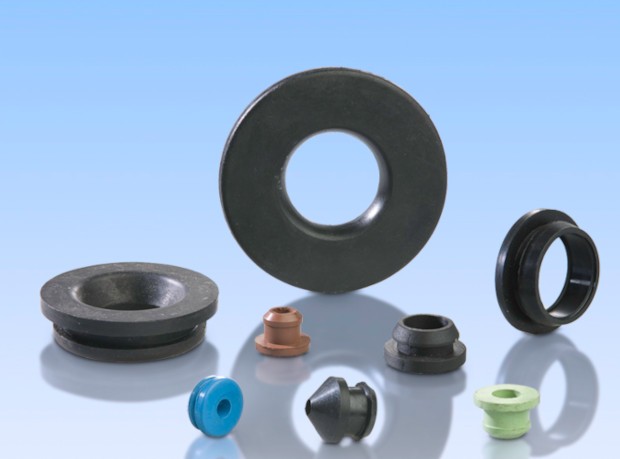
Richiamami
-
Area espositiva
Vieni a trovarci e
scopri tutti i nostri prodotti -
Forniture industriali
Richiedi un preventivo per la fornitura
di grandi quantitativi -
ISO 9001
Prodotti di qualità
e certificazione ISO 9001:2015 -
SUPPORTO MULTILINGUA
Rispondiamo in Italiano,
Inglese e Tedesco